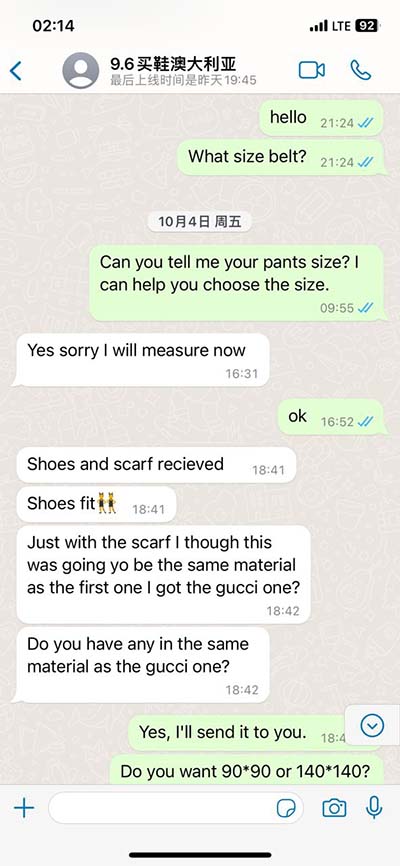
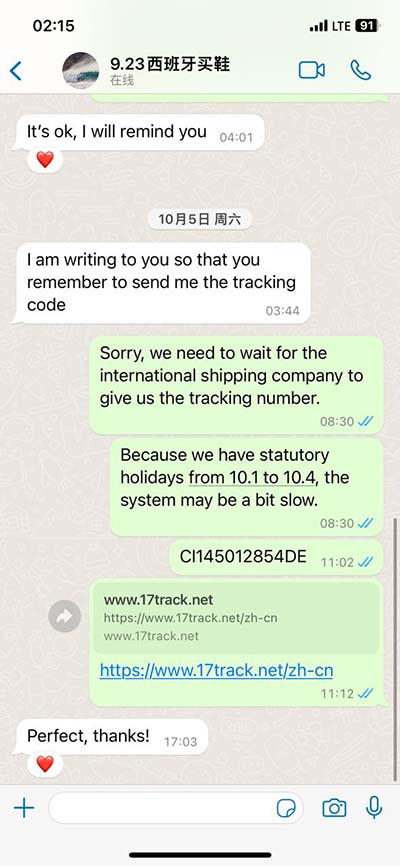
lv relaxation abnormality | impaired relaxation mitral inflow pattern lv relaxation abnormality Anyone may develop diastolic dysfunction, but you are more likely to get it if you are: 1. Older than 70. 2. Physically inactive. 3. Smokeor use tobacco products. . See more Level Description Level 1 An ally deals 20% DAS more damage and has 35% more of its original health. Level 2 An ally deals 30% DAS more damage and has 40% more of its original health. Level 3 An ally deals 40% DAS more damage and has 45% more of its original health. Level 4 An ally deals 50% DAS more damage and has 50% more of its .
0 · is impaired Lv relaxation dangerous
1 · impaired relaxation mitral inflow pattern
2 · impaired early left ventricular relaxation
3 · impaired Lv relaxation treatment
4 · impaired Lv relaxation symptoms
5 · impaired Lv relaxation stage 1
6 · impaired Lv relaxation on echo
7 · diastolic filling pattern impaired relaxation
District One Kitchen & Bar - Updated 2024, Fusion Restaurant in Las Vegas, NV. See all 20 photos. Overview. Photos. Menu. Reviews. District One Kitchen & Bar. 4.5. 15 Reviews. $30 and under. Fusion / Eclectic. Top Tags: Innovative. Good for groups. Great for creative cocktails. What is District One?
prada point-toe leather knee-high boots
Diastolic dysfunction is a problem with diastole, the first part of your heartbeat. During diastole, your lower heart chambers (ventricles) relax as they fill with blood. Diastolic dysfunction may occur when your ventricles are stiff and don’t relax properly. When this happens, your ventricles don’t fill with blood as they . See moreAnyone may develop diastolic dysfunction, but you are more likely to get it if you are: 1. Older than 70. 2. Physically inactive. 3. Smokeor use tobacco products. . See more
As your top heart chambers continue to try to pump blood into your ventricles, you may experience pressure buildup. In turn, you may have fluid and pressure . See moreDiastolic dysfunction is common in older adults. Some experts estimate that about half of all adults over age 70 have some level of diastolic dysfunction. It’s less . See more Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) is a condition that affects your heart’s ability to fill up with blood before sending the blood out into your circulation. Your heartbeat has.Disturbance in ventricular relaxation results in the disruption of pressure conditions in the left ventricle. Ventricular pressure should drop rapidly and substantially during diastole, but if .
prada white high heel
When your heart isn’t able to relax fast enough, it’s called diastolic dysfunction (DD). DD is dangerous and is believed to be associated with congestive heart failure . LV relaxation abnormality is likely to precede LV stiffening or systolic dysfunction during the development of chronic heart failure and has been assigned as a sensitive sign of . A normal filling pattern in community-dwelling subjects indicates an excellent prognosis. 1 In contrast, an abnormal filling pattern and progressively greater abnormalities of . The authors discuss possible mechanisms by which systolic loading may differently alter LV isovolumetric relaxation in normal and in failing hearts: restoring forces, .
Diastolic dysfunction is when the heart’s ventricles abnormally stiffen, which prevents the ventricles from relaxing as they should and prevents them from filling up. This . Patients with heart failure and a normal ejection fraction have significant abnormalities in active relaxation and passive stiffness. In these patients, the .
Abnormal relaxation results in prolongation of the IVRT, decrement of −dP/dt, and longer tau index. The most common parameter is the time constant of isovolumic pressure decay (tau, τ, millisecond). Diastolic dysfunction is a problem with diastole, the first part of your heartbeat. Typically, your lower heart chambers relax and fill with blood during diastole. Diastolic dysfunction occurs when your lower heart chambers don’t relax as they should. Over time, the dysfunction can lead to diastolic heart failure. Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) is a condition that affects your heart’s ability to fill up with blood before sending the blood out into your circulation. Your heartbeat has.Disturbance in ventricular relaxation results in the disruption of pressure conditions in the left ventricle. Ventricular pressure should drop rapidly and substantially during diastole, but if relaxation is impaired, the drop in pressure will be slower and less pronounced.
When your heart isn’t able to relax fast enough, it’s called diastolic dysfunction (DD). DD is dangerous and is believed to be associated with congestive heart failure symptoms in patients who have what’s called preserved left ventricular ejection fraction, according to cardiologist Wael Jaber, MD. Advertisement. LV relaxation abnormality is likely to precede LV stiffening or systolic dysfunction during the development of chronic heart failure and has been assigned as a sensitive sign of LV dysfunction. Quantitative Assessment of LV Relaxation.
A normal filling pattern in community-dwelling subjects indicates an excellent prognosis. 1 In contrast, an abnormal filling pattern and progressively greater abnormalities of left filling (impaired relaxation versus pseudonormalized and restricted filling patterns) indicate patients with a progressively increased risk of subsequent mortality.
The authors discuss possible mechanisms by which systolic loading may differently alter LV isovolumetric relaxation in normal and in failing hearts: restoring forces, intracellular calcium handling, additional crossbridge recruitment, nonuniformity, and . Diastolic dysfunction is when the heart’s ventricles abnormally stiffen, which prevents the ventricles from relaxing as they should and prevents them from filling up. This disrupts the flow of blood to and from the organs of the body. Patients with heart failure and a normal ejection fraction have significant abnormalities in active relaxation and passive stiffness. In these patients, the pathophysiological cause of elevated.Abnormal relaxation results in prolongation of the IVRT, decrement of −dP/dt, and longer tau index. The most common parameter is the time constant of isovolumic pressure decay (tau, τ, millisecond).
Diastolic dysfunction is a problem with diastole, the first part of your heartbeat. Typically, your lower heart chambers relax and fill with blood during diastole. Diastolic dysfunction occurs when your lower heart chambers don’t relax as they should. Over time, the dysfunction can lead to diastolic heart failure. Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) is a condition that affects your heart’s ability to fill up with blood before sending the blood out into your circulation. Your heartbeat has.Disturbance in ventricular relaxation results in the disruption of pressure conditions in the left ventricle. Ventricular pressure should drop rapidly and substantially during diastole, but if relaxation is impaired, the drop in pressure will be slower and less pronounced.
When your heart isn’t able to relax fast enough, it’s called diastolic dysfunction (DD). DD is dangerous and is believed to be associated with congestive heart failure symptoms in patients who have what’s called preserved left ventricular ejection fraction, according to cardiologist Wael Jaber, MD. Advertisement. LV relaxation abnormality is likely to precede LV stiffening or systolic dysfunction during the development of chronic heart failure and has been assigned as a sensitive sign of LV dysfunction. Quantitative Assessment of LV Relaxation.
A normal filling pattern in community-dwelling subjects indicates an excellent prognosis. 1 In contrast, an abnormal filling pattern and progressively greater abnormalities of left filling (impaired relaxation versus pseudonormalized and restricted filling patterns) indicate patients with a progressively increased risk of subsequent mortality. The authors discuss possible mechanisms by which systolic loading may differently alter LV isovolumetric relaxation in normal and in failing hearts: restoring forces, intracellular calcium handling, additional crossbridge recruitment, nonuniformity, and . Diastolic dysfunction is when the heart’s ventricles abnormally stiffen, which prevents the ventricles from relaxing as they should and prevents them from filling up. This disrupts the flow of blood to and from the organs of the body.
Patients with heart failure and a normal ejection fraction have significant abnormalities in active relaxation and passive stiffness. In these patients, the pathophysiological cause of elevated.
is impaired Lv relaxation dangerous
impaired relaxation mitral inflow pattern
impaired early left ventricular relaxation

5 Answers. Sorted by: 26. It is not something I would do online but I think it is possible. I guess you are using ext4. umount /home. $ umount /home. shrink the /home filesystem. $ fsck -f /dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_home. $ resize2fs /dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_home 80G. shrink the /home logical volume. $ lvreduce -L .
lv relaxation abnormality|impaired relaxation mitral inflow pattern